How The Paleo Diet® Improves Health
The Paleo Diet®, aka, The Human-Friendly Diet.
In “diet” circles, there are lots of opinions around what we should eat. But when you test everything using the scientific method, as Dr. Loren Cordain and our team have been doing for 30 years, you can be considerably more sure.
About 500 peer-reviewed research studies have convinced us that The Paleo Diet® is the healthiest, most bio-optimal way of eating. It’s the way humans ate for hundreds of thousands of years — compared to how we’ve been eating for the past 10,000 or so years. In fact, 70% of the foods in our Western diet didn’t exist more than 200 years ago.
Our general poor health, tendency to carry extra weight, and myriad food allergies and sensitivities tell us something could be a lot better.

What's Better About The Paleo Diet®?
How The Paleo Diet® Improves Health
See more on how The Paleo Diet® can help you by reducing inflammation, boosting immunity, and avoiding disease and improving disease symptoms.
LEARN MOREHow to Avoid Disease and Stay Healthy for Life
Adopting a Paleo Diet and lifestyle can help to reverse the damaging effects of modern living. Learn what steps to take today to improve your health in the long run! READCan The Paleo Diet Protect Against Chronic Diseases?
Chronic diseases have surpassed infectious diseases as the primary threat to human health. See how Paleo can prevent CNCDs. READCan the Paleo Diet Diminish Alzheimer’s Disease Risk?
For years, many scientists and pharmacists supported the amyloid cascade theory as the cause for Alzheimer’s. However, a growing body of research is disproving this theory. READHow to Heal Leaky Gut with a Diet of Paleo Foods
Heal leaky gut by eating the right foods for gut health. READGroundbreaking Research Finds The Paleo Diet® Most Effective at Improving Markers of Chronic Illness
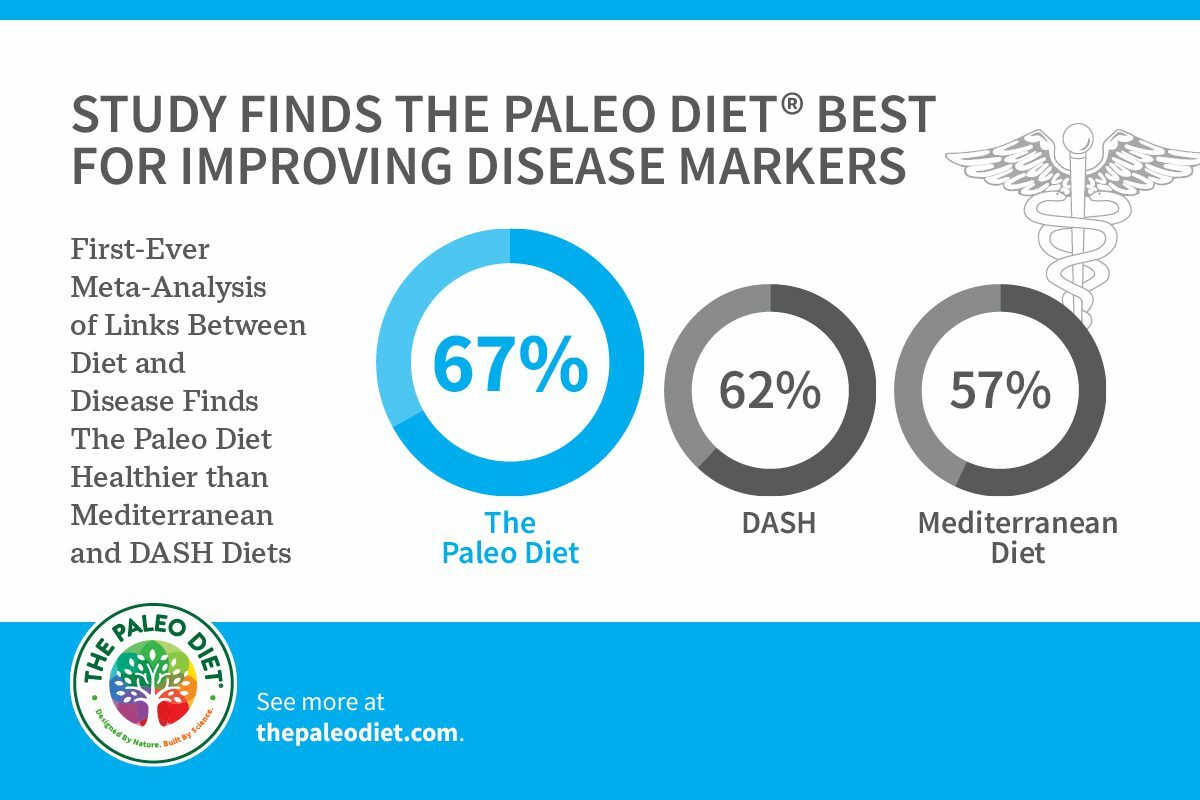
A recent, large-scale meta-analysis shows The Paleo Diet® is better than the Mediterranean and DASH diets for overall control of cholesterol, glycemic control, and inflammation.