Evolution and High Protein Diets Part 2

Did you miss Evolution and High Protein Diets Part 1? Click Here to Read It!
The Evolutionary Evidence
The fossil evidence
A number of lines of evidence suggest that meat eating and high protein diets have been a component of human nutrition since the very origins of our genus Homo. Beginning approximately 2.6 million years ago (MYA), the hominin species that eventually led to Homo began to include more animal food in their diet. A number of lines of evidence support this viewpoint.
First, the very first stone tools (Oldowan lithic technology) appear in the fossil record 2.6 MYA, 28 and there is clear cut evidence to show that these tools were used to butcher and disarticulate animal carcasses. 29, 30 Stone tool cut marks on the bones of prey animals and evidence for marrow extraction appear concurrently in the fossil record with the development of Oldowan lithic technology by at least 2.5 MYA (Figure 2). 30 It is not entirely clear which specific early hominin species or group of species manufactured and used these earliest of stone tools; however, Australopithecus garhi may have been a likely candidate. 30, 31
The development of stone tools and the increased dietary reliance on animal foods allowed early African hominins to colonize northern latitudes outside of Africa where plant foods would have been seasonally restricted. Early Homo skeletal remains and Oldowan lithic technology appear at the Dmanisi site in the Republic of Georgia (40° N) by 1.75 MYA, 32 and more recently Oldowan tools dating to 1.66 MYA have been discovered at the Majuangou site in North China (40° N). 33 Both of these tool-producing hominins would likely have consumed considerably more animal food than pre-lithic hominins living in more temperate African climates, and it is likely the majority of their daily energy was obtained from animal foods during winter and early spring when plant food sources would have been scarce or unavailable.
The genetic evidence
In addition to the fossil evidence suggesting a trend for increased animal food consumption, hominins may have experienced a number of genetic adaptations to animal-based diets early in our genus’s evolution analogous to those of obligate carnivores such as felines. Carnivorous diets reduce evolutionary selective pressures that act to maintain certain anatomical and physiological characteristics needed to process and metabolize high amounts of plant foods. In this regard, hominins, like felines, have experienced a reduction in gut size and metabolic activity along with a concurrent expansion of brain size and metabolic activity as they included more energetically dense animal food into their diets. 16, 34, 35
Further, similar to obligate carnivores, 36 humans maintain an inefficient ability to chain elongate and desaturate 18 carbon fatty acids to their product 20 and 22 carbon fatty acids. 37 Since 20 and 22 carbon fatty acids are essential cellular lipids, then evolutionary reductions in desaturase and elongase activity in hominins indicate that preformed dietary 20 and 22 carbon fatty acids (found only in animal foods) were increasingly incorporated in lieu of their endogenously synthesized counterparts derived from 18 carbon plant fatty acids.
Finally, our species has a limited ability to synthesize the biologically important amino acid, taurine, from precursor amino acids, 38, 39 and vegetarian diets in humans result in lowered plasma and urinary concentrations of taurine. 40 Like felines 41, 42 the need to endogenously synthesize taurine may have been evolutionarily reduced in humans because exogenous dietary sources of preformed taurine (found only in animal food) had relaxed the selective pressure formerly requiring the need to synthesize this conditionally essential amino acid.
Another genetic adaptation to a high meat diet involves the metabolism of purines. Purines are the nitrogenous base pairs which form the structural cross rung molecules of both DNA and RNA. As DNA and RNA are broken down within cells, the purines then can be metabolized into uric acid by the liver and a few other tissues within the body. The liver receives purines from two sources: 1) the diet, and 2) the daily breakdown of the body’s own tissues. About ⅔ of the daily purine load comes from the body’s turnover of cells, while ⅓ comes from the diet. 43 When the combined purine load (from both diet and turnover of the body’s own cells) exceeds the kidney’s ability to excrete it, blood concentrations of uric acid rise, thereby increasing the risk for gout, a painful disease caused by formation of uric acid crystals in the joints.
Although high protein, meat based diets contain high amounts of purines and would be expected to promote gout symptoms, protein ingestion actually decreases blood uric acid levels by increasing uric acid excretion. 44 This seemingly paradoxical effect occurs because the kidney increases its excretion of uric acid when faced with elevated dietary purines. 45 But more importantly, over the course of evolution, humans have evolved a genetic mutation which tends to prevent uric acid synthesis in the liver. Humans avoid the overproduction of uric acid in the face of increasing dietary purine intake from meats by decreasing the activity of an enzyme called xanthine oxidoreductase, 46 a key catalyst in the final synthesis of uric acid. Compared to other animals, xanthine oxidase activity is almost 100 times lower in humans. 47 This evolutionary adaptation has occurred because the gene coding for xanthine oxidoreductase has been repressed. 48 The final proof of the pudding has been borne out by dietary interventions showing that high protein, low glycemic load diets actually normalized serum uric acid concentrations in 7 of 12 gout patients and significantly decreased gout attacks. 49
The Isotopic Fossil Evidence
Since the evolutionary split between hominins and pongids (apes) approximately 7 million years ago, the available evidence shows that all species of hominins ate an omnivorous diet composed of minimally processed, wild-plant and animal foods. In support of this view is the omnivorous nature of chimpanzees, the closest living pongid link to hominins. Although chimpanzees (Pan paniscus and Pan troglodytes), our genetically closest nonhuman relatives, primarily consume a frugivorous diet, they still eat a substantial amount of meat obtained throughout the year from hunting and scavenging. 50-52 Observational studies of wild chimpanzees demonstrate that during the dry season meat intake is about 65g per day for adults. 51 Accordingly, it is likely that the very earliest hominins would have been capable of obtaining animal food through hunting and scavenging in a manner similar to chimpanzees.
Carbon isotope data also support the notion that early hominins were omnivorous. By about 3 million years ago MYA Australopithecus africanus obtained a significant portion of food from C4 sources (grasses, particularly seeds and rhizomes; sedges; invertebrates, including locusts and termites; grazing mammals; and perhaps even insectivores and carnivores). 53 Other fossils of early African hominins, including Australopithecus robustus and Homo ergaster, maintain carbon isotope signatures characteristic of omnivores. 54, 55 The finding of C4 in Australopithecus robustus fossils refutes the earlier view that this hominin was vegetarian. 54
There is little evidence to the contrary that animal foods have always played a significant role in the diets of all hominin species. Increased reliance on animal foods not only allowed for enhanced encephalization (brain expansion relative to body weight) and its concomitant behavioral sophistication, 16, 34, 35 but this dietary practice also permitted colonization of the world outside of Africa. An unresolved issue surrounding hominin diets is the relative amounts of plant and animal foods that were typically consumed.
Before the advent of Oldowan lithic technology about 2.6 MYA, quantitative estimates of hominin energy intake from animal food sources are unclear, other than they were likely similar to, or greater than, estimated values (4%–8.5% total energy) for chimpanzees. 51, 56 Although all available data point to increasing animal food consumption following the arrival of stone tool technology, the precise contribution of either animal or plant food energy to is unclear. Obviously, then as now, no single (animal/plant) subsistence ratio would have been necessarily representative of all populations or species of hominins. However, there are a number of lines of evidence which suggest more than half (>50%) of the average daily energy intake for most Paleolithic hominin species and populations of species was obtained from animal foods.
Richards, Pettitt, and colleagues 57 have examined stable isotopes (δ13C and δ15N) in two Neanderthal specimens (~28,000—29,000 years ago) from Vindija Cave in northern Croatia and contrasted these isotopic signatures to those in fossils of herbivorous and carnivorous mammals from the same ecosystem. The analysis demonstrated that Neanderthals, similar to wolves and arctic foxes, behaved as top-level carnivores, obtaining all of their protein from animal sources. 57 More recent studies of corroborate this earlier work and points to Neanderthals “as top predators in an open environment, with little variation through time and space,” 58 and “the percentage of plants in the Neanderthal diet must have been close to zero.” 59 Because Neanderthals were not direct predecessors of modern humans, 60 it may be more relevant to examine the isotopic data from fully modern humans living during the Pleistocene. An analysis was made of five Upper Paleolithic Homo sapiens specimens dated to ~11,700–12,380 years ago from Gough’s and Sun Hole Caves in Britain. 61 The data indicated these hunter-gatherers were consuming animal protein year-round at a higher trophic level than the artic fox.
All of these studies 57-62 could be criticized as not being representative of typical hominin diets, as these two species lived in climates and ecosystems that fostered an abundance of large, huntable mammals, which were preyed upon preferentially. Additional clues to the typical plant-to-animal subsistence ratio in Paleolithic hominin diets can be found in the foraging practices of historically studied hunter-gatherers.
The ethnographic evidence
Our analysis (Figure 3) of the Ethnographic Atlas data 62 showed that the dominant foods in the majority of historically studied hunter-gatherer diets were derived from animal food sources. 14 Most (73%) of the world’s hunters-gatherers obtained >50% of their subsistence from hunted and fished animal foods, whereas only 14% of worldwide hunter-gatherers obtained >50% of their subsistence from gathered plant foods. For all 229 hunter-gatherer societies, the median subsistence dependence on animal foods was 56% to 65%. In contrast, the median subsistence dependence on gathered plant foods was 26% to 35%. 14
The major limitation of ethnographic data is that the preponderance of it is subjective in nature, and the assigned scores for the five basic subsistence economies in the Ethnographic Atlas are not precise, but rather are approximations. 63 Fortunately, more exact, quantitative dietary studies were carried out on a small percentage of the world’s hunter gatherer societies. 15, 64
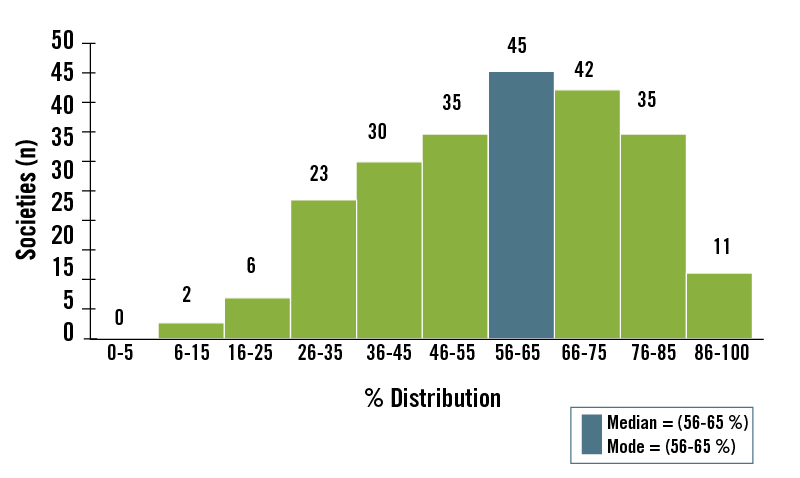
Table 1 lists these studies and shows the plant-to-animal subsistence ratios by energy. The average score for animal food subsistence is 65%, while that for plant-food subsistence is 35%. These values are similar to our analysis of the entire (n = 229) sample of hunter-gatherer societies listed in the Ethnographic Atlas in which the mean score for animal food subsistence was 68% and that for plant food was 32%. 14
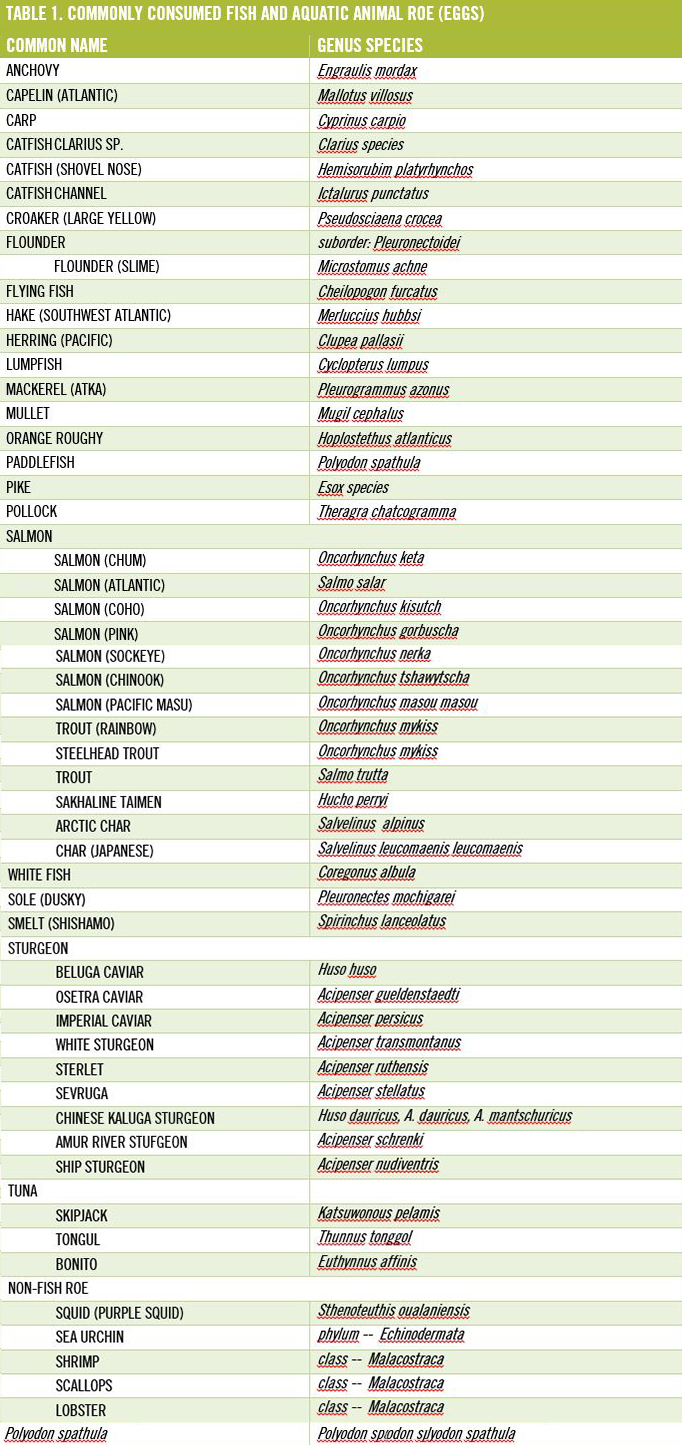
When the two polar hunter-gatherer populations, who have no choice but to eat animal food because of the inaccessibility of plant foods, are excluded from Table 1 the mean score for animal subsistence is 59% and that for plant-food subsistence is 41%. These animal-to-plant subsistence values fall within the same respective class intervals (56%–65% for animal food; 26%–35% for plant food) as those we estimated from the ethnographic data when the confounding influence of latitude was eliminated. 14 Consequently, there is remarkably close agreement between the quantitative data in Table 1 and the ethnographic data 14 that animal food comprised more than half of the energy in historically studied hunter-gatherer diets.
Based upon hunter gatherer plant to animal subsistence ratios and the known macronutrient contents of wild plant and animal foods, it is possible to estimate the macronutrient content of these diets. 14 The typical hunter-gatherer protein intake would have fallen between 19 and 35% of total energy, 14 values which would be labeled either “high” or “very high” protein diets when compared to current U.S. values (15%).
Consequently, when framed in an evolutionary context, current western dietary protein intakes fall outside the range of diets that would have conditioned the human genome for nearly 2 million years. The evolutionary template would then suggest that when dietary protein intakes are restored to levels that our species is genetically accustomed, good health will prevail. Conversely, lower or higher values likely result in ill health.
Let’s see what the experimental evidence shows in Evolution and High Protein Diets Part 3 of The Evolutionary Basis for the Therapeutic Effects of High Protein Diets Series.
References
Part 1 & Part 2
[1]. Bogert LJ, Briggs GM, Calloway DH. Nutrition and Physical Fitness, Ninth Edition. W.B. Sauders Company, Philadelphia, 1973.
[2] Dyerberg J, Bang HO. A hypothesis on the development of acute myocardial infarction in Greenlanders. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1982;161:7-13.
[3] Jenkins DJ, Wolever TM, Taylor RH, Barker H, Fielden H, Baldwin JM, Bowling AC, Newman HC, Jenkins AL, Goff DV. Glycemic index of foods: a physiological basis for carbohydrate exchange. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Mar;34(3):362-6.
[4] No authors listed. Position paper on trans fatty acids. ASCN/AIN Task Force on Trans Fatty Acids. American Society for Clinical Nutrition and American Institute of Nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1996 May;63(5):663-70.
[5] National Academy of Sciences, Institute of Medicine. Letter Report on Dietary Reference Intakes for Trans Fatty Acids, 2002. //www.iom.edu/CMS/5410.aspx.
[7] Willett WC, Stampfer MJ. Rebuilding the food pyramid. Sci Am. 2003 Jan;288(1):64-71
[8] Krauss RM, Eckel RH, Howard B, et al. Dietary Guidelines: revision 2000: A statement for healthcare professionals from the Nutrition Committee of the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2000 Oct 31;102(18):2284-99.
[9] Blanck HM, Gillespie C, Serdula MK, Khan LK, Galusk DA, Ainsworth BE .Use of low-carbohydrate, high-protein diets among americans: correlates, duration, and weight loss. MedGenMed. 2006 Apr 5;8(2):5.
[10] Ornish D. Dr. Dean Ornish’s Program for Reversing Heart Disease: The Only System Scientifically Proven to Reverse Heart Disease Without Drugs or Surgery. New York : Random House, 1990.
[11] Nesse RM, Stearns SC, Omenn GS. Medicine needs evolution. Science 2006;311:1071.
[12] Dobzhansky T. Am Biol Teacher. 1973 March; 35:125-129.
[13] Cordain L, Eaton SB, Sebastian A, Mann N, Lindeberg S, Watkins BA, O’Keefe JH, Brand-Miller .Origins and evolution of the Western diet: health implications for the 21st century. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005 Feb;81(2):341-54.
[4] Cordain L, Miller JB, Eaton SB, Mann N, Holt SH, Speth JD. Plant-animal subsistence ratios and macronutrient energy estimations in worldwide hunter-gatherer diets. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 Mar;71(3):682-92.
[15] Cordain L, Eaton SB, Brand Miller J, Mann N, Hill K. The paradoxical nature of hunter-gatherer diets: Meat based, yet non-atherogenic. Eur J Clin Nutr 2002; 56 (suppl 1):S42-S52.
[16] Cordain L, Watkins BA, Mann NJ. Fatty acid composition and energy density of foods available to African hominids: evolutionary implications for human brain development. World Rev Nutr Diet 2001, 90:144-161.
[17] Bravata DM, Sanders L, Huang J, Krumholz HM, Olkin I, Gardner CD, Bravata DM. Efficacy and safety of low-carbohydrate diets: a systematic review.
JAMA. 2003 Apr 9;289(14):1837-50.
[18] St Jeor ST, Howard BV, Prewitt TE, Bovee V, Bazzarre T, Eckel RH et al.. Dietary protein and weight reduction: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Nutrition Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism of the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2001 Oct 9;104(15):1869-74.
[19] Wright JD, J Kennedy-Stephenson J, Wang CY, McDowell MA, Johnson CL, National Center for Health Statistics, CDC. Trends in intake of energy and macronutrients—United States, 1971-2000. JAMA. 2004;291:1193-1194.
[20] McDowell M, Briefel R, Alaimo K, et al. Energy and macronutrient intakes of persons ages 2 months and over in the United States: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, Phase 1, 1988–91. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office, Vital and Health Statistics; 1994. CDC publication No. 255.
[21] Rudman D, DiFulco TJ, Galambos JT, Smith RB 3rd, Salam AA, Warren WD. Maximal rates of excretion and synthesis of urea in normal and cirrhotic subjects.J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2241-9.
[22] peth JD, Spielmann KA. Energy source, protein metabolism, and hunter-gatherer subsistence strategies. J Anthropological Archaeology 1983;2:1-31.
[23] Speth JD. Early hominid hunting and scavenging: the role of meat as an energy source. J Hum Evol 1989;18:329-43.
[24] Noli D, Avery G. Protein poisoning and coastal subsistence. J Archaeological Sci 1988;15:395-401.
[25] Lieb CW. The effects on human beings of a twelve months’ exclusive meat diet. JAMA 1929;93:20-22.
[26] Ogden CL, Fryar CD, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. Mean body weight, height and body mass index, United States 1960—2002 . Center for Disease Control. Advance Data from Vital and Health Statistics, No. 347, October 27, 2004.
[27] Oliver WJ, Cohen EL, Neel JV. Blood pressure, sodium intake, and sodium related hormones in the Yanomamo Indians, a “no-salt” culture. Circulation. 1975 Jul;52(1):146-51.
[28]Semaw S, Rogers MJ, Quade J, Renne PR, Butler RF, Dominguez-Rodrigo M, Stout D, Hart WS, Pickering T, Simpson SW. 2.6-Million-year-old stone tools and associated bones from OGS-6 and OGS-7, Gona, Afar, Ethiopia. J Hum Evol. 2003 Aug;45(2):169-77.
[29]Bunn, HT, Kroll EM. Systematic butchery by Plio-Pleistocene hominids at Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania. Curr Anthropol 1986;20:365–398.
[30]de Heinzelin J, Clark JD, White T, Hart W, Renne P, WoldeGabriel G, Beyene Y, Vrba E. Environment and behavior of 2.5-million-year-old Bouri hominids. Science. 1999 Apr 23;284(5414):625-9
[31]Asfaw B. White T, Lovejoy O, Latimer B, Simpson S, Suwa, G. Australopithecus garhi: A new species of early hominid from Ethiopia. Science 1999; 284, 629–635.
[32]Vekua A, Lordkipanidze D, Rightmire GP, Agusti J, Ferring R, Maisuradze G, Mouskhelishvili A, Nioradze M, De Leon MP, Tappen M, Tvalchrelidze M, Zollikofer C. A new skull of early Homo from Dmanisi, Georgia. Science. 2002 Jul 5;297(5578):85-9.
[32]Zhu RX, Potts R, Xie F. Hoffman KA, Deng CL, Shi CD, Pan YX, Wang HQ, Shi, RP, Wang YC, Shi GH, Wu NQ. New evidence on the earliest human presence at high northern latitudes in northeast Asia. Nature 2004; 431: 559–562.
[33]Aiello LC, Wheeler P. The expensive tissue hypothesis. Curr Anthropol 1995; 36:199–222.
[34]Leonard W.R, Robertson ML. Evolutionary perspectives on human nutrition: The influence of brain and body size on diet and metabolism. Am J Hum Biol 1994; 6: 77–88.
[35]Pawlosky R., Barnes A., Salem, N. Essential fatty acid metabolism in the feline: Relationship between liver and brain production of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Lipid Res 1994;35: 2032–2040.
[36]Hussein N, Ah-Sing E, Wilkinson P, Leach C, Griffin BA, Millward DJ. Long-chain conversion of [13C] linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid in response to marked changes in their dietary intake in men. J Lipid Res. 2005 Feb;46(2):269-80.
[37]Sturman JA, Hepner GW, Hofmann AF, Thomas PJ. Metabolism of [35S] taurine in man. J Nutr. 1975 Sep;105(9):1206-14.
[38]Chesney RW, Helms RA, Christensen M, Budreau AM, Han X, Sturman JA. The role of taurine in infant nutrition. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998;442:463-76.
[39]Laidlaw SA, Shultz TD, Cecchino JT, Kopple JD. Plasma and urine taurine levels in vegans. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988 Apr;47(4):660-3.
[40]Knopf K, Sturman JA, Armstrong M, Hayes KC. 1978. Taurine: An essential nutrient for the cat. J Nutr 1978;108: 773–778.
[41]MacDonald ML, Rogers QR, Morris JG. Nutrition of the domestic cat, a mammalian carnivore. Annu Rev Nutr 1984; 4: 521–562.
[42]Fam AG. Gout: excess calories, purines, and alcohol intake and beyond. Response to a urate-lowering diet. J Rheumatol. 2005 May;32(5):773-7.
[43]Matzkies F, Berg G, Madl H. The uricosuric action of protein in man. Adv Exp Med Biol 1980;122A:227-31.
[44]Loffler W. Grobner W, Medina R, Zollner N. Influence of dietary purines on pool size, turnover, and excretion of uric acid during balance conditions. Isotope studies using 15N-uric acid. Res Exp Med (Berl). 1982(2):113-123.
[45]Oda M, Satta Y, Takenaka O, Takahata N. Loss of urate oxidase activity in hominoids and its evolutionary implications. Mol Biol Evol. 2002 May; 19(5): 640-53.
[46]Abadeh S, Killacky J, Benboubetra M, Harrison R. Purification and partial characterization of xanthine oxidase from human milk. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 21;1117(1):25-32
[47]Xu P, LaVallee P, Hoidal JR. Repressed expression of the human xanthine oxidoreductase gene. E-box and TATA-like elements restrict ground state transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem. 2000 Feb 25;275(8):5918-26.
[48]Dessein PH, Shipton EA, Stanwix AE, Joffe BI, Ramokgadi J. Beneficial effects of weight loss associated with moderate calorie/carbohydrate restriction, and increased proportional intake of protein and unsaturated fat on serum urate and lipoprotein levels in gout: a pilot study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Jul;59(7):539-43.
[49]vTeleki G. The omnivorous chimpanzee. Sci Am 1973; 228: 33–42.
[50]Stanford CB. The hunting ecology of wild chimpanzees: Implications for the evolutionary ecology of Pliocene hominids. Am Anthropol 1996; 98: 96–113.
[51]Schoeninger MJ, Moore J, Sept JM. Subsistence strategies of two “savanna” chimpanzee populations: The stable isotope evidence. Am J Primatol 1999: 49: 297–314.
[52]van der Merwe NJ, Thackeray JF, Lee-Thorp JA, Luyt J. The carbon isotope ecology and diet of Australopithecus africanus at Sterkfontein, South Africa J Hum Evol 2003;44: 581–597.
[53]Lee-Thorp J, Thackeray JF, van der Merwe N. The hunters and the hunted revisited. J Hum Evol 2000; 39: 565–576.
[54]Sponheimer M, Lee-Thorp JA.. Differential resource utilization by extant great apes and australopithecines: Towards solving the C4 conundrum. Comp Biochem Physiol A 2003;136: 27–34.
[55]Sussman RW. Foraging patterns of nonhuman primates and the nature of food preferences in man. Fed Proc 1978;37: 55–60.
[56]Richards MP, Pettitt PB, Trinkaus E, Smith FH, Paunovic M, Karavanic, I. Neanderthal diet at Vindija and Neanderthal predation: The evidence from stable isotopes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2000;97: 7663–7666.
[57]Bocherens H, Drucker DG, Billiou D, Patou-Mathis M, Vandermeersch B. Isotopic evidence for diet and subsistence pattern of the Saint-Cesaire I Neanderthal: review and use of a multi-source mixing model. J Hum Evol. 2005 Jul;49(1):71-87
[58]Balter V, Simon L. Diet and behavior of the Saint-Cesaire Neanderthal inferred from biogeochemical data inversion. J Hum Evol. 2006 Oct;51(4):329-38.
[59]Currat M, Excoffier L. Modern humans did not admix with Neanderthals during their range expansion into Europe. PLoS Biol. 2004 Dec;2(12):e421. Epub 2004 Nov 30
[60]Richards MP, Hedges REM, Jacobi R, Current, A, Stringer C. Focus: Gough’s Cave and Sun Hole Cave human stable isotope values indicate a high animal protein diet in the British Upper Palaeolithic. J Archaeol Sci 2000;27: 1–3.
[61]Gray JP. A corrected ethnographic atlas. World Cult J 1999;10: 24–85.
[62]Hayden B. Subsistence and ecological adaptations of modern hunter/gatherers. In: RSO Harding, RSO, Teleki G. (Eds.), Omnivorous Primates. Columbia University Press, New York, 1981, pp. 344–421.
[63]Kaplan H, Hill K, Lancaster J, Hurtado AM. A theory of human life history evolution: diet, intelligence, and longevity. Evol. Anthropol 2000;9:156–185.




