Surprising Foods to Avoid on the AIP Diet

Reviewed by Dr. Mark J. Smith on March 7, 2022
Are you trying an Autoimmune Protocol (AIP) Diet? Autoimmune diets are related to The Paleo Diet®, and if you are already following The Paleo Diet, you’ve essentially cut back on (or completely eliminated) most foods that cause problems for those with autoimmune diseases, like grains and refined sugar. However, there are some surprising foods to avoid on the AIP diet, even though they are Paleo-approved.
What Is the Autoimmune Protocol Diet?
The Autoimmune Protocol Diet, or AIP for short, is a type of elimination diet. It was created to help reduce inflammation, pain, fatigue, and other symptoms of autoimmune disease. [1]
An AIP diet is built around the premise that certain foods can irritate the gut and trigger an autoimmune response that can then induce symptoms.
How Does the AIP Diet Work?
The AIP diet works in phases. The first phase of the AIP diet eliminates specific foods for 30 to 90 days, or whenever symptoms seem to improve.
See our guide: How to Start an Autoimmune Protocol Diet.
The second phase gradually reintroduces those foods one at a time in order to identify which foods may be causing a response and/or symptoms.
Non-Paleo Foods Eliminated on the AIP Diet
- Grains. Regardless of whether they’re whole grains (with the entire grain kernel intact) or refined grains (processed so that fiber, iron and vitamins are stripped away), grains are off the table on AIP.[2] This is because grains, and especially wheat, are not easily tolerated by many people, and they contribute to chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases. [3]
- Dairy. Anything made with cow’s or goat’s milk, like cheese and yogurt, should be avoided. Dairy contains certain proteins that can trigger inflammation. [4] Plus, lactose intolerance is a common condition.
- Legumes. Beans, peas, lentils, soy, peanuts, and other legumes are high in lectins. Lectins are anti-nutrients that are hard to digest and may damage the gut barrier, entering into our blood. They can also inhibit the absorption of some minerals. People who may have underlying digestive or autoimmune issues may experience a worse reaction from eating lectin-containing foods than others. [5] Legumes also contain phytic acid that can also decrease the absorption of some minerals and slow digestion. [6]
- Sugar. Anything made with white cane sugar or high fructose corn syrup, like candy or soda, is off the table on AIP. Sugar is highly processed and devoid of nutrients, and eating too much is associated with inflammation, high blood pressure, weight gain, insulin resistance, and fatty liver disease. [7]
- Processed foods. These unnatural foods contain refined sugars, sodium, trans fats, artificial coloring and flavorings, processed oils, and more. Frozen meals, instant foods, packaged bread, and fast food are just a few examples of processed foods. They’re also generally low in fiber and other nutritional content. They contribute to a host of health issues, especially for those with underlying autoimmune disorders. [8]
Surprising Paleo Foods to Avoid on The AIP Diet
While most of the foods that are eliminated on AIP are also not Paleo, there are a few foods that we eliminate on AIP that are normally Paleo-approved.
Here are a few of these generally healthy foods, and why they should be eliminated in the first phase of the AIP diet.
Egg Whites
For most people, eggs are a healthy addition to their diet. But to a person with an autoimmune disease, eggs (especially egg whites) may cause issues.
The enzyme, or protein, in egg whites called lysozyme can cross the gut barrier, carrying with it other proteins that the body will respond to as foreign. Individuals with an autoimmune disease are more sensitive and will have a larger inflammatory response to these foreign proteins attached to lysozymes. [9]
In addition, egg whites have a high incidence of allergy-related symptoms. Although this is mainly about egg whites, egg yolks can also be a common food sensitivity so they too are on the elimination phase of the AIP Diet. Chances are egg yolks will be better tolerated when reintroducing foods than egg whites.
What to eat instead: We have lots of egg-free breakfast recipes to try instead of your daily scramble. If you’re baking, replace eggs with coconut oil, applesauce, pumpkin puree, or avocado.
See our guide: How to Be Paleo When You Can’t Eat Eggs.
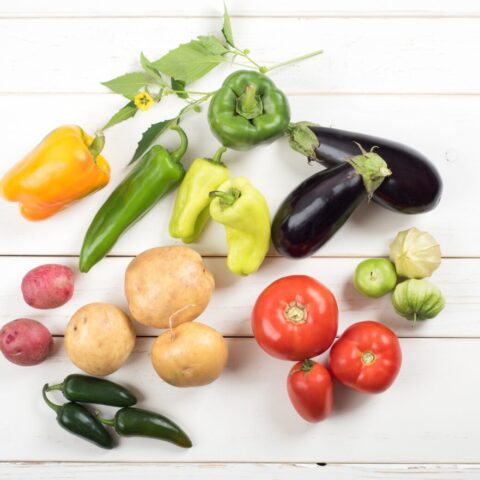
Eggplant
Although eggplant is highly nutritious food, it’s on the elimination list of the AIP Diet because they are considered a nightshade plant. Nightshades contain certain compounds (like lectins, saponins and capsaicin) that may cause irritation in the gut and worsen issues from an already present autoimmune disease.
However, there is great debate on whether these highly nutritious nightshades actually induce inflammation at all. This is why the elimination phase of the AIP diet is so important. If they cause no issues, nightshades should be reintroduced in the second phase of the diet and not avoided. [10]
See our guide: How to Tell If You Have a Nightshade Sensitivity
What to eat instead: Try using zucchini or yellow squash in place of eggplant.
Peppers
Just like eggplant, peppers are considered nightshades. Yes, this includes both bell peppers and hot peppers! Seasonings such as cayenne, paprika and red pepper flakes should also be avoided.
What to eat instead: Try using yellow squash in place of bell peppers, or use ground ginger as a seasoning.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are also nightshades, meaning they should also be avoided on the elimination phase of the AIP Diet for the same reasons as eggplants and peppers.
What to eat instead: Depending on what you’re making, veggies like cucumber, carrots, celery or zucchini can be a good stand-in. You can also swap your tomato sauces for olive oil and black pepper.
Bananas
For most people, bananas are not an issue. But if you have autoimmune issue, it might be worth eliminating to see how your body responds. The pulp of ripe bananas contains a molecule called thaumatin-like protein that may have similar properties to lectin. These molecules may also be responsible for allergies. [11, 12]
What to eat instead: You can snack on any other fruit. If you’re baking banana bread or something similar, try applesauce, avocado, or pumpkin puree in place of bananas.
The Bottom Line
While most foods that are eliminated in the first phase of the AIP diet are already not Paleo, there are a few extra foods you’ll want to avoid—like nightshades, eggs, and bananas.
Remember, the elimination phase is only temporary! The end goal is to give the body time to heal, to eventually tolerate some foods, and to pinpoint foods that may be a permanent issue. The reintroduction phase will look different for everybody, so be patient with yourself!
Note: It is recommended to visit a registered dietitian nutritionist before beginning any type of elimination diet. Professional support can ensure you are following the diet correctly and that all of your essential nutritional needs are being met.
References:
- Leech B, McEwen B, Sekyere EO. Diet, digestive health, and autoimmunity: The foundations to an autoimmune disease food pyramid—part 2. Altern Complement Ther. 2020;26(4):158–67. https://doi.org/10.1089/act.2020.29287.ble
- What foods are in the Grains Group? [Internet]. USDA MyPlate. [cited 2022 January 28]. https://www.myplate.gov/eat-healthy/grains
- Punder K, Pruimboom L. The Dietary Intake of Wheat and other Cereal Grains and Their Role in Inflammation. Nutrients. 2013 Mar. 5(3): 771-787. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3705319/
- Campbell T, MD. Autoimmune Disease: Genes, Infection, Environment & Gut. [Intermet] Center for Nutrition Studies. 2020 [cited 2022 February 1]. https://nutritionstudies.org/autoimmune-disease-genes-infection-environment-gut/
- Lectins [Internet]. Harvard School of Public Health/The Nutrition Source. [cited 2022 February 4]. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/anti-nutrients/lectins/
- Are Anti-Nutrients Harmful? [Internet]. Harvard School of Public Health/The Nutrition Source. [cited 2022 February 5]. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/anti-nutrients/
- The sweet danger of sugar [Internet]. Harvard Health Publishing. 2022 [cited 2022 February 4]. https://www.health.harvard.edu…;
- Fuhrman J, MD. The Hidden Dangers of Fast and Processed Food. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2018 Sept-Oct; 12(5): 375-381. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6146358/
- Sahin O, Ziaei A, Karaismailoglu E, Taheri N. The serum angiotensin converting enzyme and lysozyme levels in patients with ocular involvement of autoimmune and infectious disease. BMC Ophthalmol. 2016; 16: 19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/p…;
- What’s the Deal With Nightshade Vegetables? [Internet] ClevelandClinic.org 2019 [cited 2022 February 5]. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/whats-the-deal-with-nightshade-vegetables/
- Barre A, Peumans WJ, Menu-Bouaouiche L, Van Damme EJ, May GD, Herrera AF, Van Leuven F, Rouge P. Purification and structural analysis of an abundant thaumatin-like protein from ripe banana fruit. Planta. 2000 Nov.; 211(6): 791-9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.go…;
- Leone P, Menu-Bouaouiche, L, Peumans WJ, Pavan F, Barre A, Roussel A, Van Damme E, Rouge P. Resolution of the structure of the allergenic and antifungal banana fruit thaumatin-like protein at 1.7-A. Biochimie 2006 Jan.; 88(1): 45-52. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16085352/